This is a note for the Southeast University course “Communication Networks and Technologies” taught by Prof. Wang. In this post I will mark down the basic concepts of the communication network, multiplexing techniques and channel coding.
Overview of the Communication Network Principles
There are four main parts of the communication network:
- Terminal
- Transmission (Channel coding, Multiplexing, etc.)
- Switching
- Protocol
Now let’s go through each part in detail.
Terminal
Terminal is the end point of the communication network. For example, a cell phone, a computer, a printer, etc. are all terminals.
In the terminal, there are two main services:
-
Information Service (Terminal Service): Provided on the terminal, such as text messaging, email, voice messaging, etc. It is based on the Network Service (Bearer Service) provided by the network.
-
Network Service (Bearer Service): Data transfer from one place to another provided by the network, usually via UNI (User Network Interface).
Transmission
Transmission is the process of sending and receiving data through the communication network.
This process involves a service called Communication Service, which is highly dependent on the Multiplexing and Channel Coding techniques to achieve high data rate and low error rate.
First, let’s introduce the Multiplexing technique. The goal for this technique is: Multi-user, multi-service transmitted in one line efficiently. There are six main multiplexing techniques:
-
Frequency-Division Multiplexing (FDM): 技术简单,但每一路信道都要有独立的调制解调设备,且每个子信道分配灵活性差。
-
Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM): 抽样定理,数字化基础。位同步,帧同步,要求时钟同步。是一种同步时分复用技术。
-
Code Division Multiplexing (CDM): 利用一个码元表示各个数字链路的信号,在接收机上解码,分到各个信道去。
-
Statistical Division Multiplexing (SDM): 随机分配时隙给每一个信道。相当于异步时分复用。开销则是需要位同步,块同步。
-
Wave Division Multiplexing (WDM): 使用不同波长的光传输数据。
-
Multiple Access (MA): 即多个用户不一定在同一位置向信道传输数据。可以集成上面的五种复用方式。
Switching
Swithching is an unbreakable part of the communication network. It is the main difference between a communication system and a communication network.
Here are the three main connection methods.
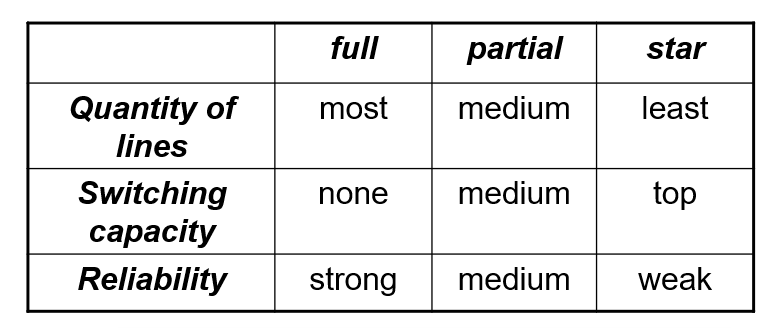
Main Switching Methods
There are three main switching methods, with the latter two can be combined as “Store and Forward” (存储转发). Note that the Multiple Access technique can also be used in the switching process. Here are the table for the main switching technologies:
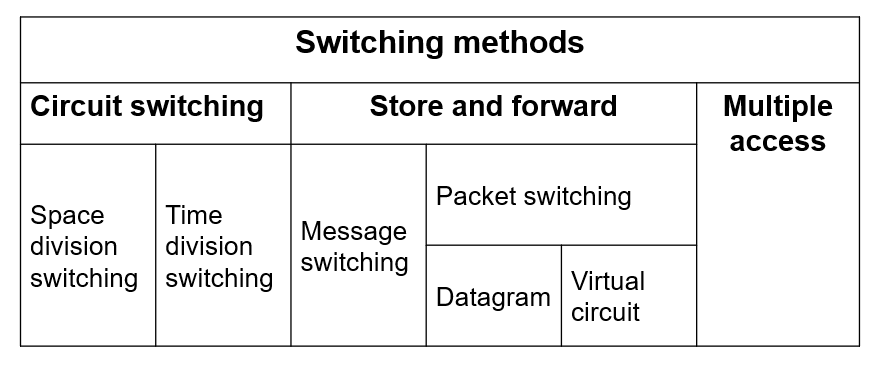
Circuit Switching
There are two main circuit switching methods: Space-division Circuit Switching and Time-division Circuit Switching. For the former, communication lines are connected according to their locations in physical space, that is, each connection is connected using a different physical line, and this line is maintained from the beginning of information exchange to the end. And for the latter, it is only implemented in TDM systems, and realize the switching function by exchanging the time slots of the communication lines.
Circuit switching has pros and cons.
The pros are:
- fixed delay
- continuous data transfer
The cons are:
- Requires a setup to establish the connection
- Data rate needs to be fixed
- unused when idle
Message Switching
Different from circuit switching, both packet switching and message switching are not based on a real circuit, or called a physical path.
Suppose a message is transmitted from host A to host B. The message switching method transmitt the message through nodes among the hosts to achieve the switching process. However, as the message length is uncertain, it is hard to control delay and registers. Therefore, it is not suitable for real-time applications.
Packet Switching
It divides the message into a series of packets, and uses pipelining to speed up the switching process. There are 2 categories according to service provided by communication sub-network:
-
Datagram Switching: Each packet is transmitted independently, and the receiver needs to reassemble the packets to get the original message.
-
Virtual Circuit Switching: All packets associated with a session follow the same path, and the route is predetermined.
Why call it “Virtual Circuit Switching”? Because they are just “logically connected” in the network, but not physically connected. Every node can have connections to multiple nodes.
Lots of things to add…
Protocol
Standards: A Uniform Protocol
It’s a must to establish a system to communicate and organize all hardware devices within the network. In telephone networks, the system is called “Signaling”, while in data networks, it is called “Network Protocol”. To make them interconnected, standard is also required. Typical standards include:
- ITU-T (International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector)
- IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
- EIA (Electronic Industries Association)
Data Communication Protocol
Error Control: Frame Error Issues
Here are the main error control techniques:
-
Forward Error Correction (FEC, 前向纠错): It is a type of redundancy technique that detects and corrects errors in data, such as LDPC codes, Hamming codes, etc.
-
Automatic Repeat ReQuest (ARQ, 自动请求重传): It is a type of error control technique that retransmits lost or corrupted data segments. It is often used in scenarios where no strict real-time communication is required. Typical ARQ Protocols are: ABP(Pure Stop and wait), Go Back N and SRP. Overview of ARQ protocols
-
Hybrid Error Correction (HEC, 混合纠错): It is a combination of FEC and ARQ, where FEC is used for detecting and correcting errors, and ARQ is used for retransmitting lost or corrupted data segments.
Flow Control: Speed lssue
Flow Control in Data link Layer
Mostly, in real life, the Data-Link Layer has no flow control, and all flow control is handled in the Transport Layer. For example, there is an ethernet flow control, but it is often not implemented, and it is poorly supported. It is an afterthought that was bolted onto ethernet.
Flow control has two basic algorithms:
- Stop and Wait - This flow control mechanism forces the sender after transmitting a data frame to stop and wait until the acknowledgement of the data-frame sent is received.
- Sliding Window - In this flow control mechanism, both sender and receiver agree on the number of data-frames after which the acknowledgement should be sent. As we learnt, stop and wait flow control mechanism wastes resources, this protocol tries to make use of underlying resources as much as possible.
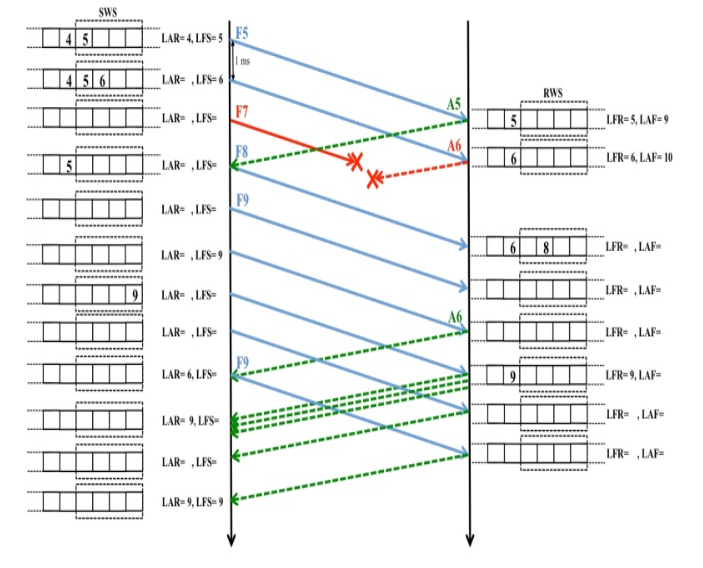
Congestion Control: Global Issue
We may use similiar techniques as flow control to solve the congestion control issue.
HDLC (High-Level Data Link Control, 高级数据链路控制) Protocol
It is a bit-oriented data link protocol.
Frame Structure description on Zhihu: HDLC Protocol
OSI-RM Model
Open System Interconnection Reference Model
r
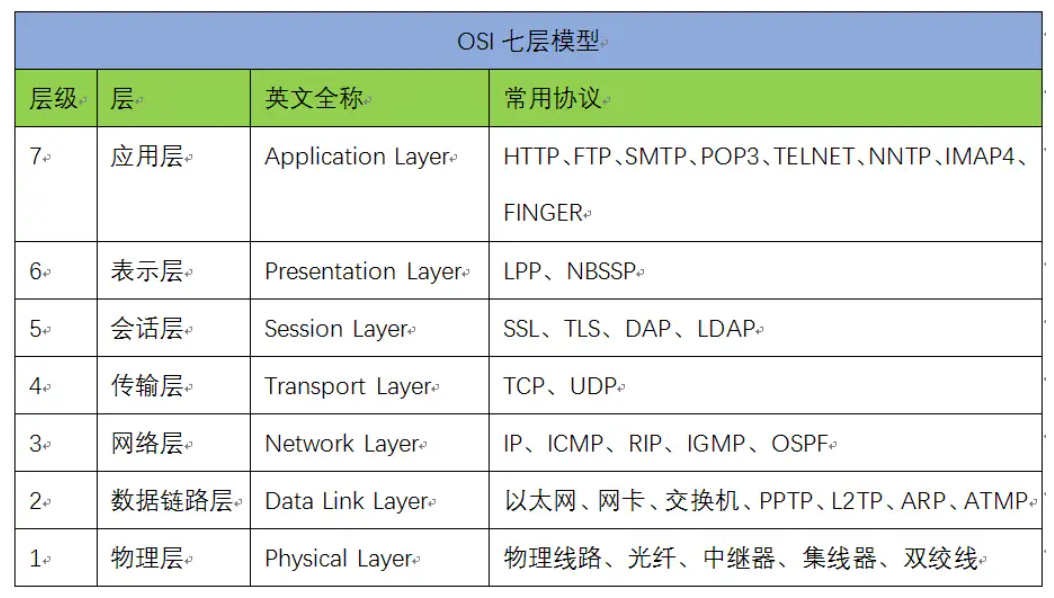
Vertically A layer provides a service to the one above, while horizontally talks to its peer using a protocol.
| Layer | Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | Application | 为应用程序或用户请求提供各种请求服务。 |
| 6 | Presentation | 数据编码、格式转换、数据加密。 |
| 5 | Session | 创建、管理和维护会话。 |
| 4 | Transport | 数据通信(End to End)、流控制、差错控制。 |
| 3 | Network | IP选址和路由选择。 |
| 2 | Data Link | 提供介质访问和链路管理。 |
| 1 | Physical | 管理通信设备和网络媒体之间的互联互通。 |
Here’s a link for reference: Protocol Layers and Service Model
Title Background Source: アスター
This one is AWESOME! I love it!